- What is Pyria disease? OR Pyria in teeth? OR Pyria meaning? OR Pyria wiki? OR Pyorrhea dental problem? OR Pyorrhea teeth problem? OR Pyria dental? OR Pyria meaning in English? OR Pyorrhea teeth disease? OR Pyria disease Wikipedia? OR Pyria disease of teeth? OR Pyria of the gum? OR Pyria mouth disease? OR What is pyria of the gums? OR What is Pyorrhea gum disease?
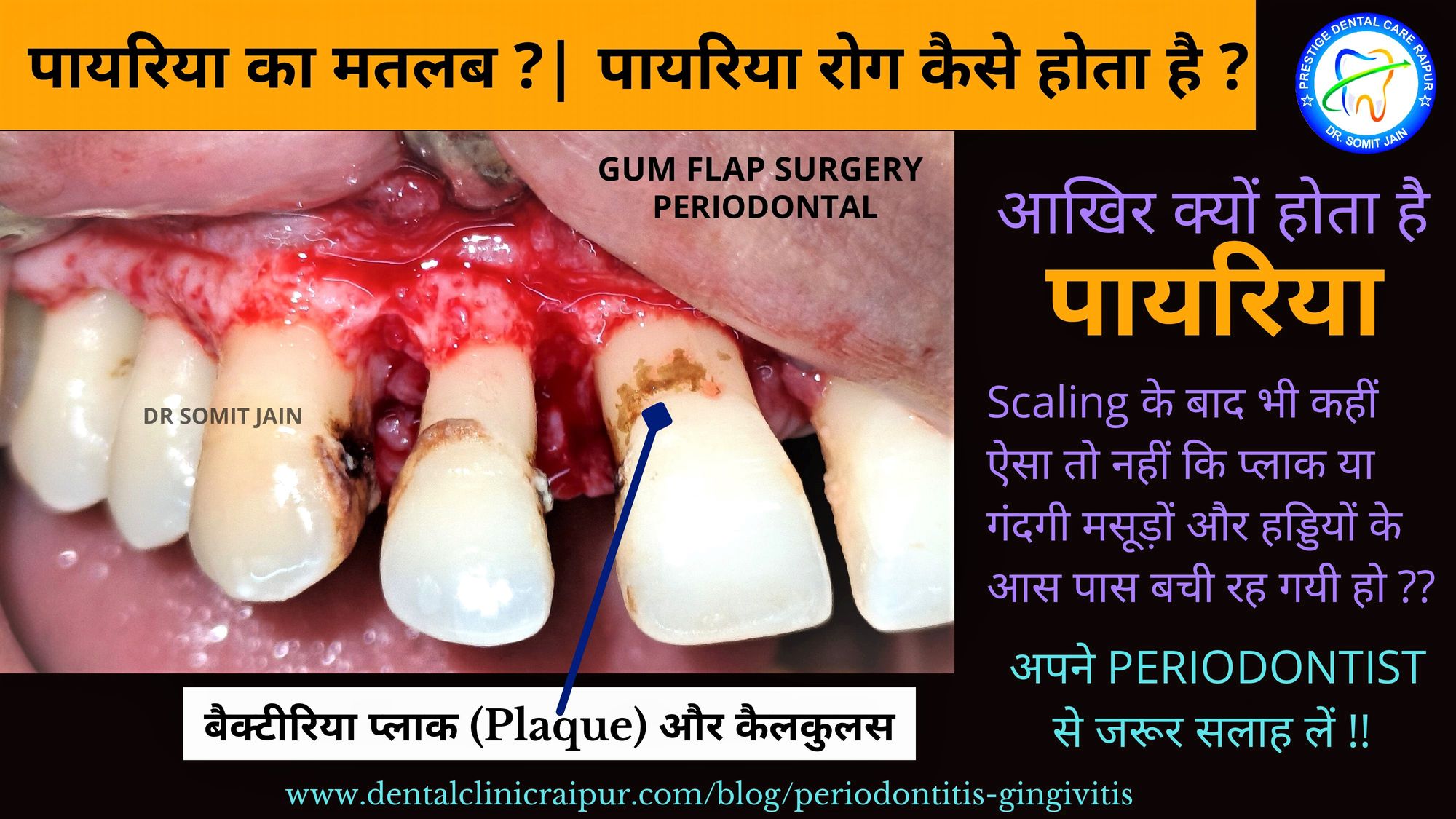
पायरिया का मतलब ? | पायरिया रोग कैसे होता है ?
INTRODUCTION :
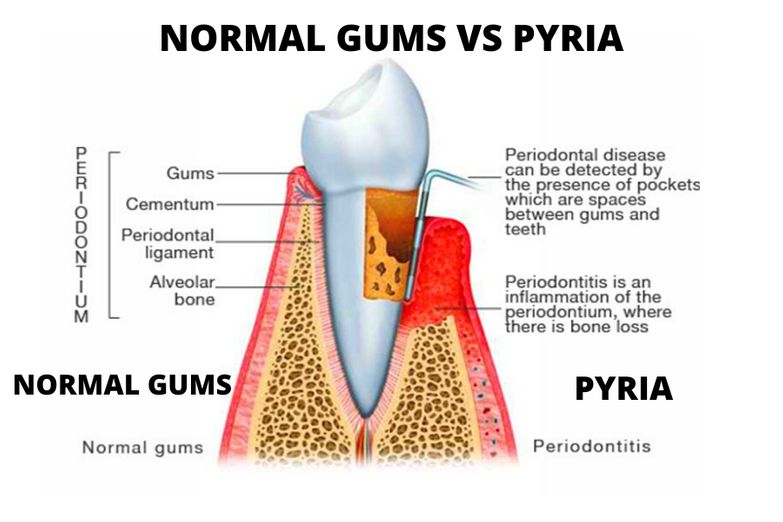
Gum disease, which is also known as Periodontal disease (Gingivitis & Periodontitis) and PYRIA is a progressive disease which if left untreated may result in tooth loss because of poor dental hygiene .
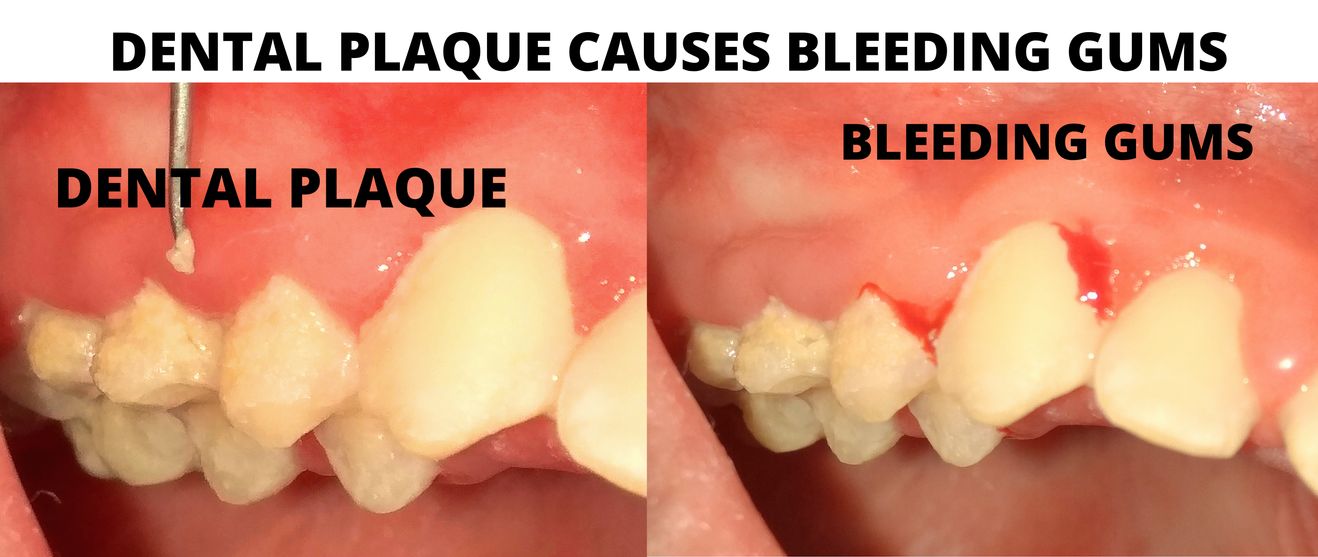
Pyria/Pyorrhea begins with the inflammation and irritation of the gingival tissues which surround and support the teeth. The cause of this inflammation is the toxins released by harmful bacteria found in plaque or biofilm.
These harmful bacteria colonize the gingival tissue and form deeper pockets between the teeth and the gums.
If treated promptly, the effects of mild inflammation (known as gingivitis) are completely reversible.
However, if the bacterial infection is allowed to progress (poor dental hygiene) or left untreated, Gingivitis may proceed to or risk of developing Periodontitis (Mild, Moderate & Severe) causing the destruction of gum tissue and the underlying jaw bone; promoting tooth loss. Hence Professional Cleaning both above and below the gum line at early stage of disease is very necessary to prevent tooth loss.
In some cases, the bacteria from this infection can travel to other areas of the body via the bloodstream causing Systemic diseases.
- In most cases, people experience NO PAIN with Pyria/Pyorrhea in early stages until the disease is very advanced. (Pyria: Don’t Wait Until it Hurts)
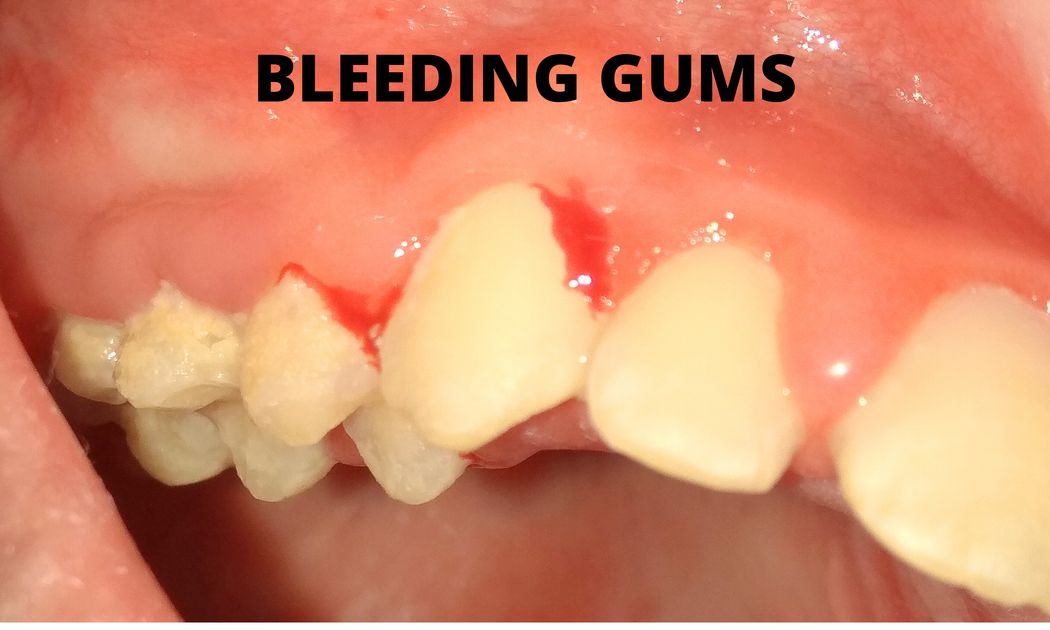
- Bleeding and swollen gums are the most common signs & symptoms of developing Pyria/Pyorrhea.
- Risk factors include Smoking, Diabetes, family history, and certain medications.
- Diagnosis is made by clinical examination of the gum tissue around the teeth both visually and with a Periodontal Probe (to rule out pockets) and X-rays (IOPA & OPG) looking for bone loss around the teeth.
- If you notice that your gums bleed on a regular basis contact Periodontist or Gum Specialist as soon as possible.
- Regular dental check-ups and proactive preventive good oral hygiene are the best methods for preventing Pyria/Pyorrhea.
Why the term "Pyorrhea Alveolaris" a MISNOMER ??
- The word “Pyorrhea” comes from the Greek pyorrhoia, “discharge of pus” i.e. it is not restricted to the diseases of the teeth.
- “Pyorrhea Alveolaris” : Purulent inflammation of the gums and tooth sockets, often leading to loosening of the teeth. A discharge of pus.
- “Pyorrhea Alveolaris” /Pyria term is usually employed to designate all diseased conditions of the investing tissues of the teeth, and as such is a misnomer. (Drea et al 1919)
- Such a term as “Pyorrhea Alveolaris” is wrong because, for one reason, it is likely to mislead the patient, dentist, and physician. If there is failure to find pus, no such condition as that described by “Pyorrhea Alveolaris” is present. But there may be infection and chronic
inflammation present that may be just as serious as, and in some cases terminate in, the suppurating condition described as pyorrhea. - And because this non suppurative condition is not properly recognized and described, it is too frequently overlooked and dismissed from mind or not properly treated, both by the dental and the medical adviser. The result is that instead of arresting these periodontal problems in their incipiency they are allowed to progress to a point where it is next to impossible or impossible to get rid of them without extracting the teeth.
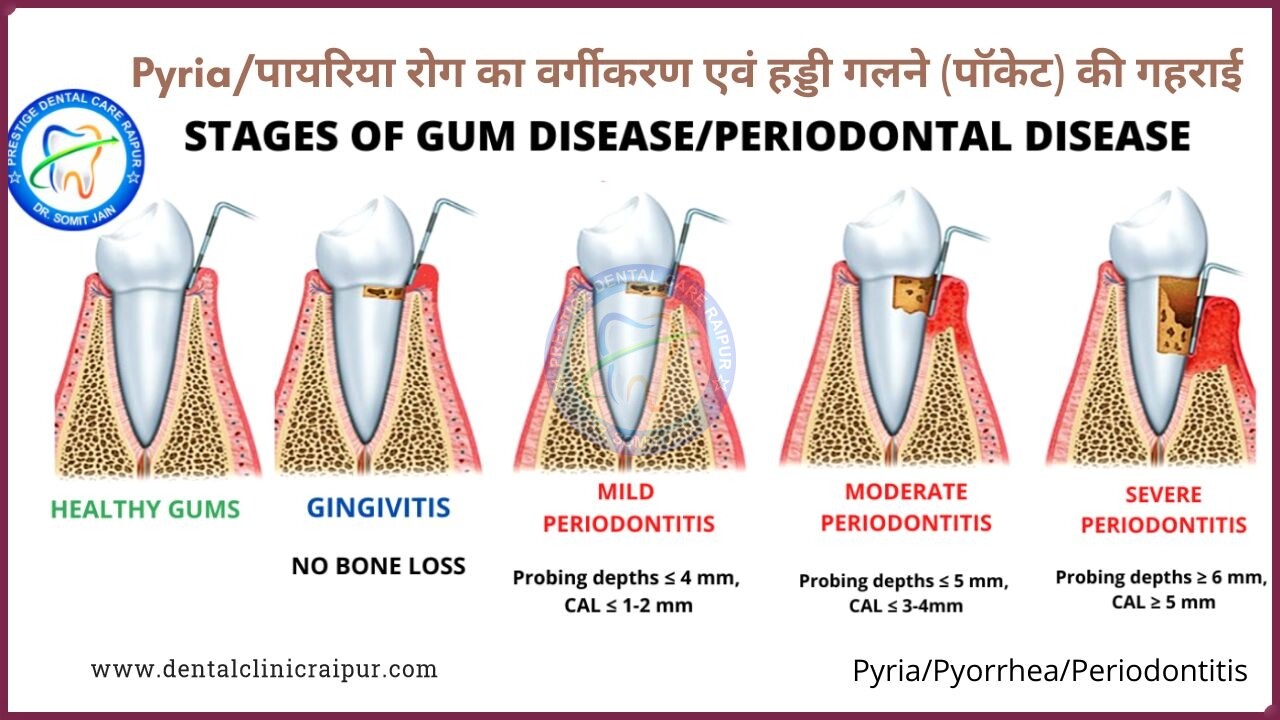
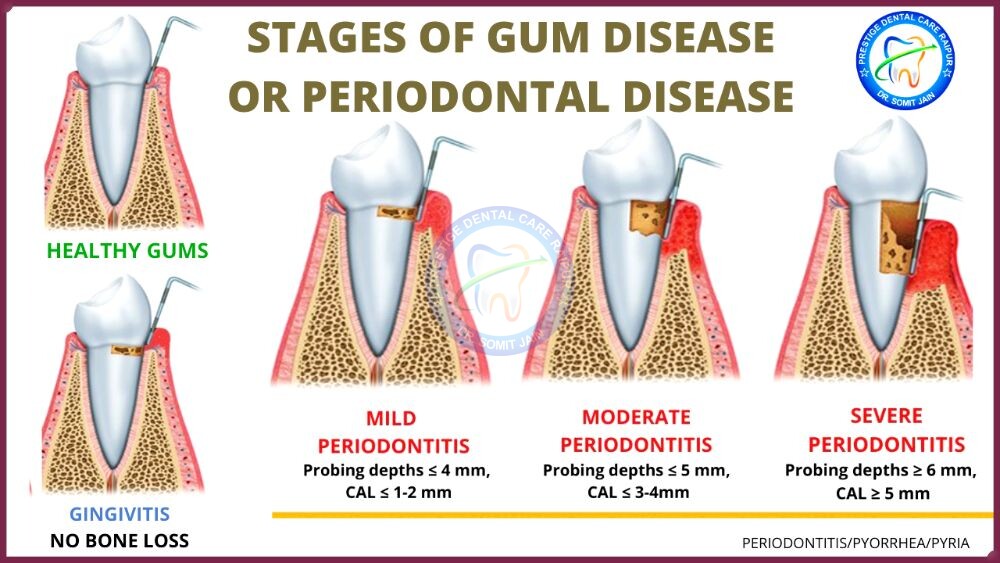
- When the disease is limited to the gum tissue, it may be referred to as Gingivitis.
- When this has progressed so far that there is involvement of the cementum, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone, it may be referred to as Periodontitis.
पायरिया रोग कैसे होता है ?


What is Pyria ??
- Periodontal disease or Pyria begins with the inflammation and irritation of the gingival/gum tissues which surround and support the teeth. The cause of this inflammation is the toxins released by harmful bacteria found in plaque or biofilm.
- Throughout the day a thin layer called dental plaque forms over your teeth, this is known as Biofilm. This is a sticky and natural layer made up primarily of bacteria.


2. What is Pyria in hindi? OR Pyorrhea teeth problem in hindi? OR Pyria meaning in hindi? OR Pyorrhea dental problem in hindi?
Prestige Dental Care Raipur के Dr Somit Jain बताते है की PYRIA/PYORRHEA or पायरिया का सामान्य अर्थ “दांत के चारों ओर सूजन” का होना है, दाँत की सतह के आसपास सूक्ष्मजीव, जैसे बैक्टीरिया (Bacteria) मौजूद रहते हैं, और यही बैक्टीरिया पायरिया रोग का कारण बनते है। जिससे व्यक्तियों के मुंह में दुर्गन्ध (Halitosis) आना बढ़ जाती है, पायरिया के बैक्टीरिया दांतों के आस-पास मसूड़ों के ऊतकों (Gum tissues) को प्रभावित कर सूजन वाली स्थिति पैदा करता है, जिससे मसूड़े लाल हो जाते हैं, और कभी-कभी उनसे खून भी आ सकता हैं (Red & Swollen Gums)
पेरियोडोंटाइटिस (Periodontitis), मसूड़ों का एक सामान्य संक्रमण रोग है जो दांतों के मुलायम ऊतक (मसूड़ों) और हड्डी को नुकसान पहुंचाता है। यदि इसका उपचार समय पर ना किया जाये तो, दांतों के चारों ओर की हड्डी धीरे-धीरे नष्ट हो जाती है।
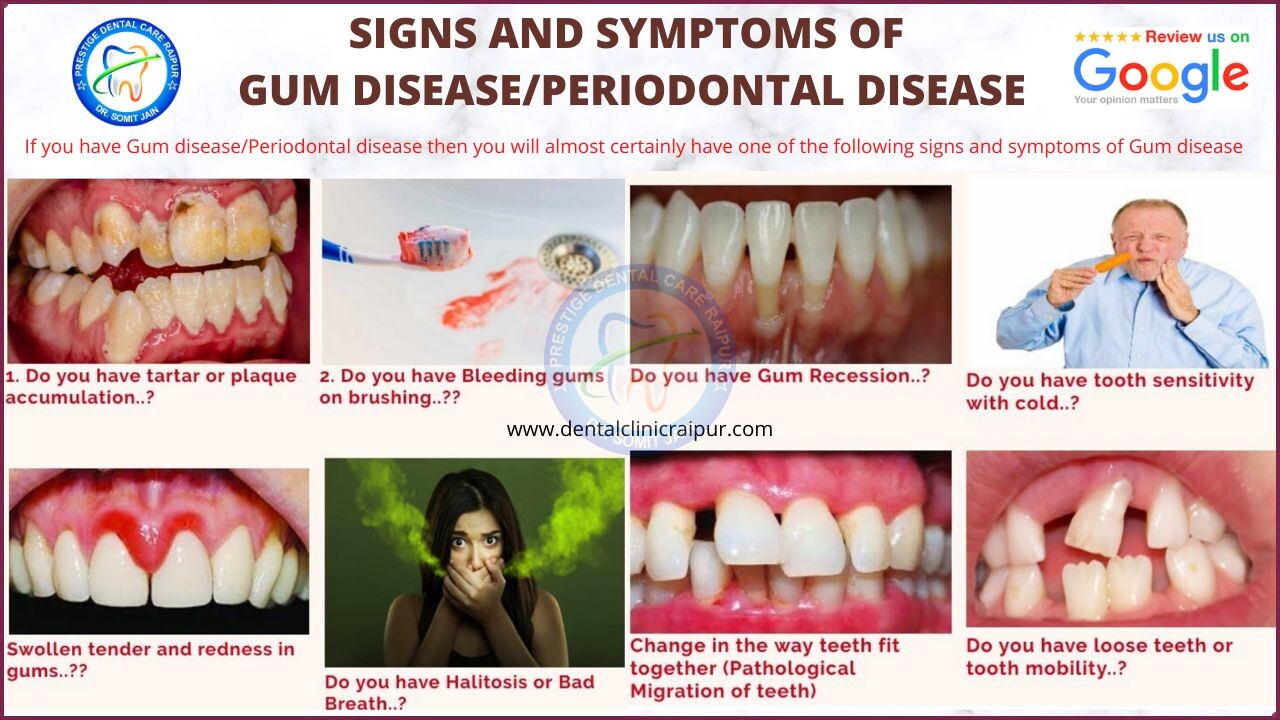
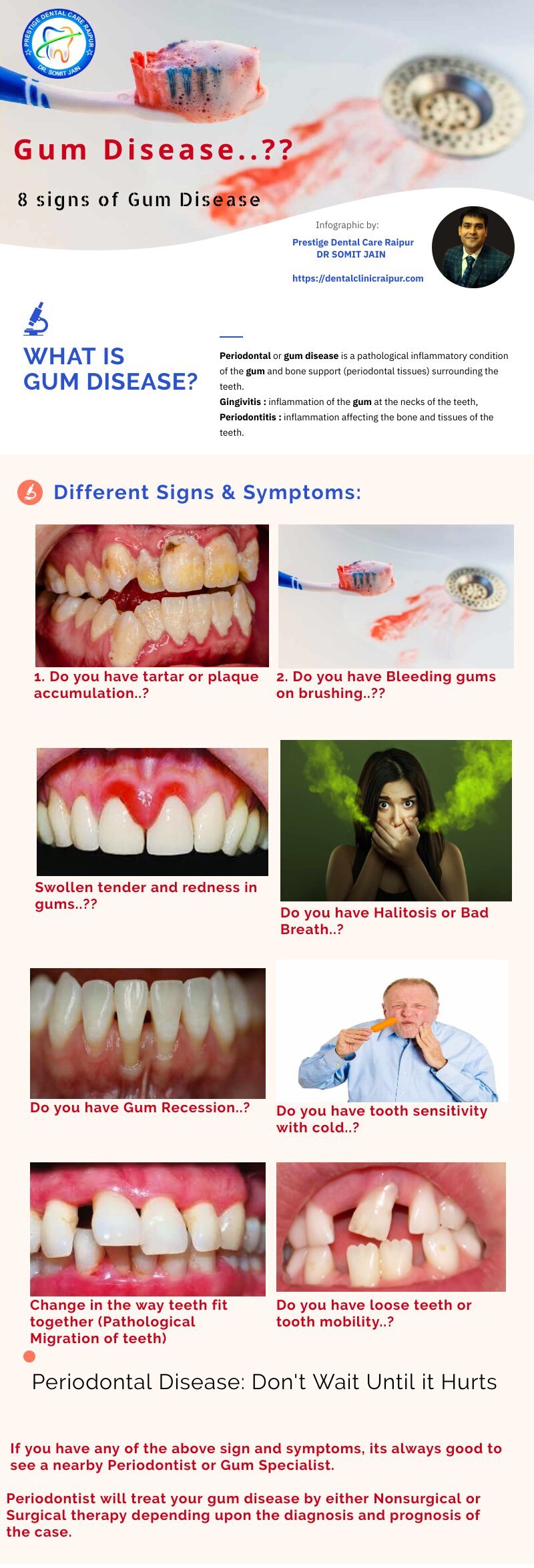
8 Warning Signs & Symptoms of Gum disease (Dental Infographics by Dr. Somit Jain)
Gum disease can be painless, so it is important to be aware of any of the following symptoms:
1. Bleeding gums when you clean your teeth (if gums bleed while brushing or flossing)
2. Soft, Swollen,sour, red or tender gums
3. Persistent bad breath or bad taste in mouth (Halitosis)
4. Any change in the way teeth come together
5. Pus from the gum line on pressing
6. Gums shrinking (pulling ) away from the teeth (Receded Gums)
7. Tooth hypersensitivity or Sensitive teeth
8. Loose teeth (Tooth Mobility)







3. What are the causes of Pyria/Pyorrhea of the gums? OR What causes Pyria gum disease OR Causes of pyria?
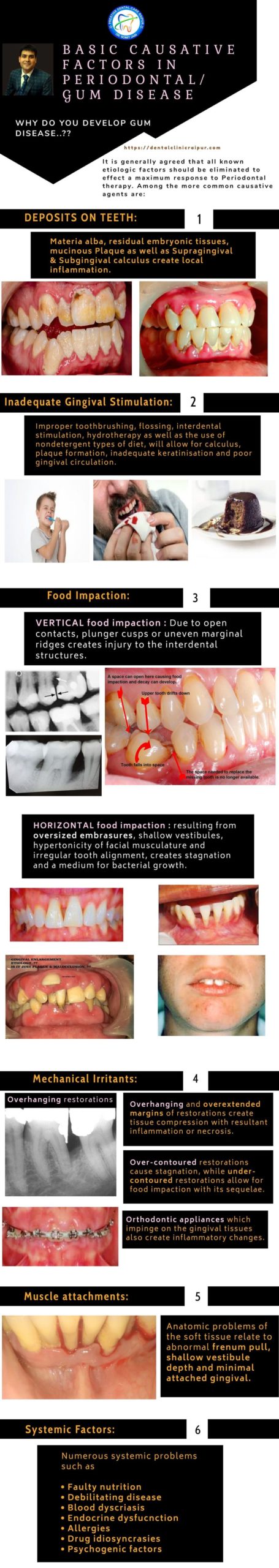
CAUSES OF PYRIA/PYORRHEA
It is generally agreed that all known etiologic factors should be eliminated to effect a maximum response to Periodontal therapy. Among the more common causative agents are:
- DEPOSITS ON TEETH: Materia alba, residual embryonic tissues, mucinous Plaque (biofilm formation with bacteria) as well as Supragingival and Subgingival calculus create local inflammation.
- Inadequate Gingival Stimulation: Improper toothbrushing, flossing, interdental stimulation, hydrotherapy as well as the use of nondetergent types of diet, will allow for calculus, plaque biofilm formation, inadequate keratinisation and poor gingival circulation.
- Food Impaction
- Vertical food impaction : Due to open contacts, plunger cusps or uneven marginal ridges creates injury to the interdental structures.
- Horizontal food impaction : resulting from oversized embrasures, shallow vestibules, hypertonicity of facial musculature and irregular tooth alignment, creates stagnation and a medium for bacterial biofilm growth.
- Overhanging and overextended margins of restorations create tissue compression with resultant inflammation or necrosis.
- Over-contoured restorations cause stagnation, while under-contoured restorations allow for food impaction with its sequelae.
- Orthodontic appliances which impinge on the gingival tissues also create inflammatory changes.
- Overzealous toothbrushing, incorrect in manner or type of brush, may allow for damage to the tooth, gingival and crestal bone.
- Mouth Breathing and Smoking often cause dehydration of the soft tissue with resultant inflammation.
- Faulty nutrition
- Debilitating disease
- Blood dyscriasis
- Endocrine dysfucnction
- Allergies
- Drug idiosyncrasies
- Psychogenic factors
Above plays important role in the etiology of Periodontal disease
CAUSES OF PYRIA/PYORRHEA IN TEETH INFORGRAPHIC


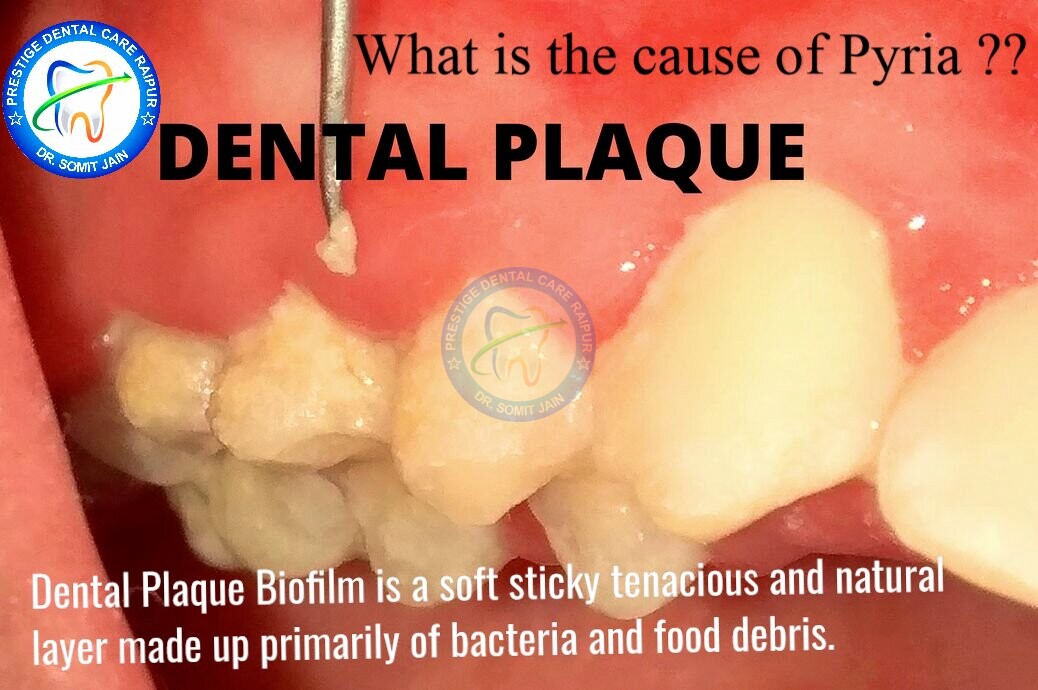
What is the cause/reason of Pyria ??
- Pyria begins with the inflammation and irritation of the gingival tissues which surround and support the teeth. The cause of this inflammation is the toxins released by harmful bacteria found in plaque or biofilm.
- This Dental Plaque Biofilm is a soft sticky tenacious and natural layer made up primarily of bacteria and food debris.






Stages of Gum Disease/Pyorrhea/Pyria




GUM (GINGIVAL) ENLARGEMENT TREATMENT
HOW TO TREAT (GET RID OF ) SWOLLEN GUMS??
HOW TO TREAT GINGIVITIS AND PERIODONTITIS??
SEVERE GUM DISEASE TREATMENT
INFLAMED GUM POCKET TREATMENT
LASER GUM TREATMENT NEAR ME
GINGIVECTOMY BEFORE AND AFTER
DEEP PERIODONTAL POCKET TREATMENT
DEEP CLEANING TEETH BEFORE AND AFTER PICTURES
PERIODONTITIS CLINIC TREATMENT
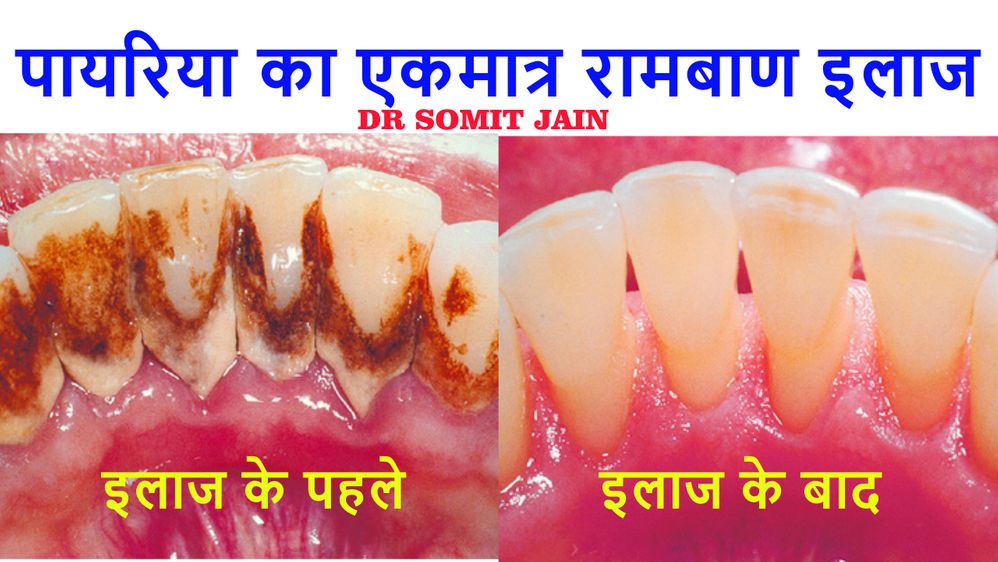
HOW TO REMOVE PYORRHEA FROM TEETH
What is the best treatment for Pyria??
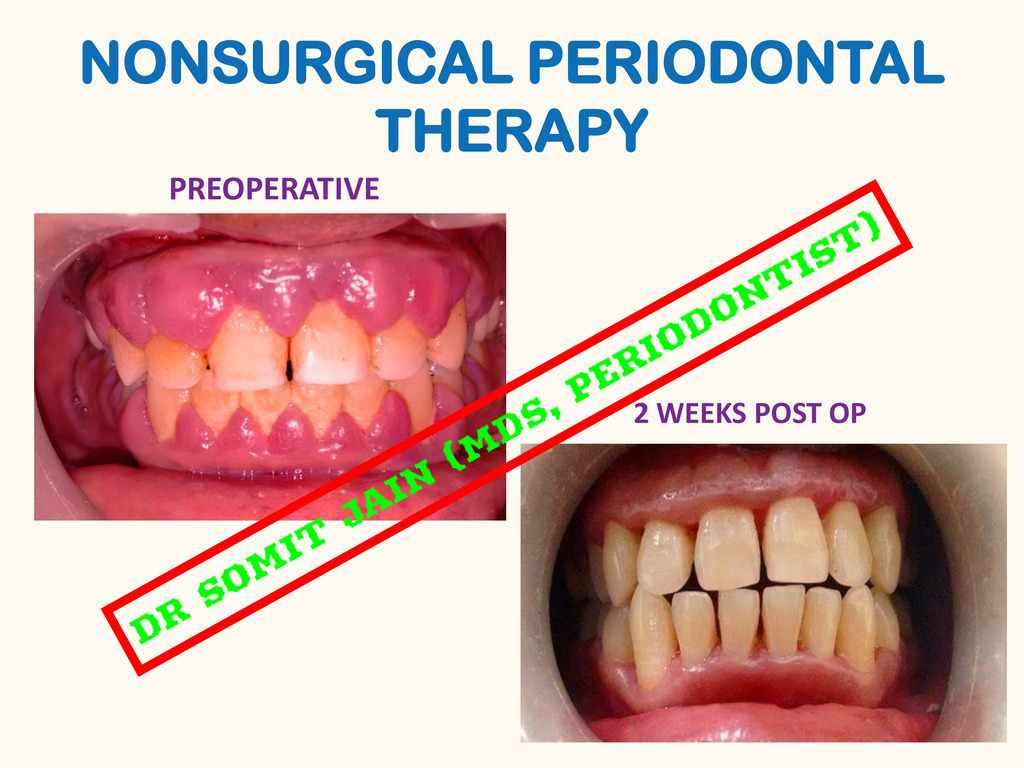


SUBGINGIVAL SCALING BEFORE AND AFTER PICTURES


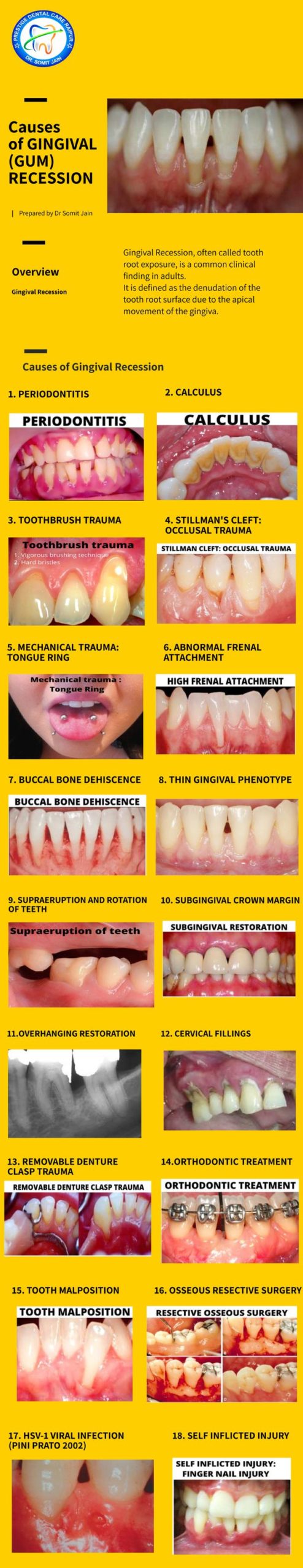
18 MAIN CAUSES OF GINGIVAL (GUM) RECESSION (INFOGRAPHICS)


Pyria or Pyorrhea Vs Systemic disease
Pyria or Periodontitis has been an associated with a number of other systemic diseases OR medical conditions including heart disease, immune system disorders, respiratory disease, chronic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, cognitive impairment, obesity, metabolic syndrome and cancer. It is important to take any medical advice if required of any underlying medical condition before proceeding with the Nonsurgical or Surgical Periodontal therapies.
Pyorrhea/Pyria Mukt Bharat



How Pyria can be cured ??
How to treat Pyria??
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day. If possible, clean oral cavity after each meal.
- Do massage of teeth and gums softly
- One of the best things you can do is swish warm, salty water around in your mouth
- Electric toothbrush to maximize your cleaning potential.
- The Waterpik Water Flosser is the only Water Flosser to earn the American Dental Association (ADA) Seal of acceptance.
- Make sure your toothbrush has soft or extra-soft bristles.
- Replace your toothbrush every three months.
- Floss daily
- Interdental brushes for orthodontic cases and natural gaps between teeth.
- Use a natural mouthwash.
- Visit your dentist at least once a year.
- Refrain from smoking or chewing tobacco.
- Limit sugar
- Oil pulling
- Exposing teeth to salt or baking soda could erode the tooth’s surface enamel over time so try to avoid that.
Can Pyria be transmitted ??
- Research has shown that Pyria/Pyorrhea is caused by the inflammatory reaction to bacteria under the gums, so pyria technically may not be contagious.
- However, the bacteria that cause the inflammatory reaction can be spread through saliva to saliva contact.
COVID Consent form for Dental treatment in Hindi





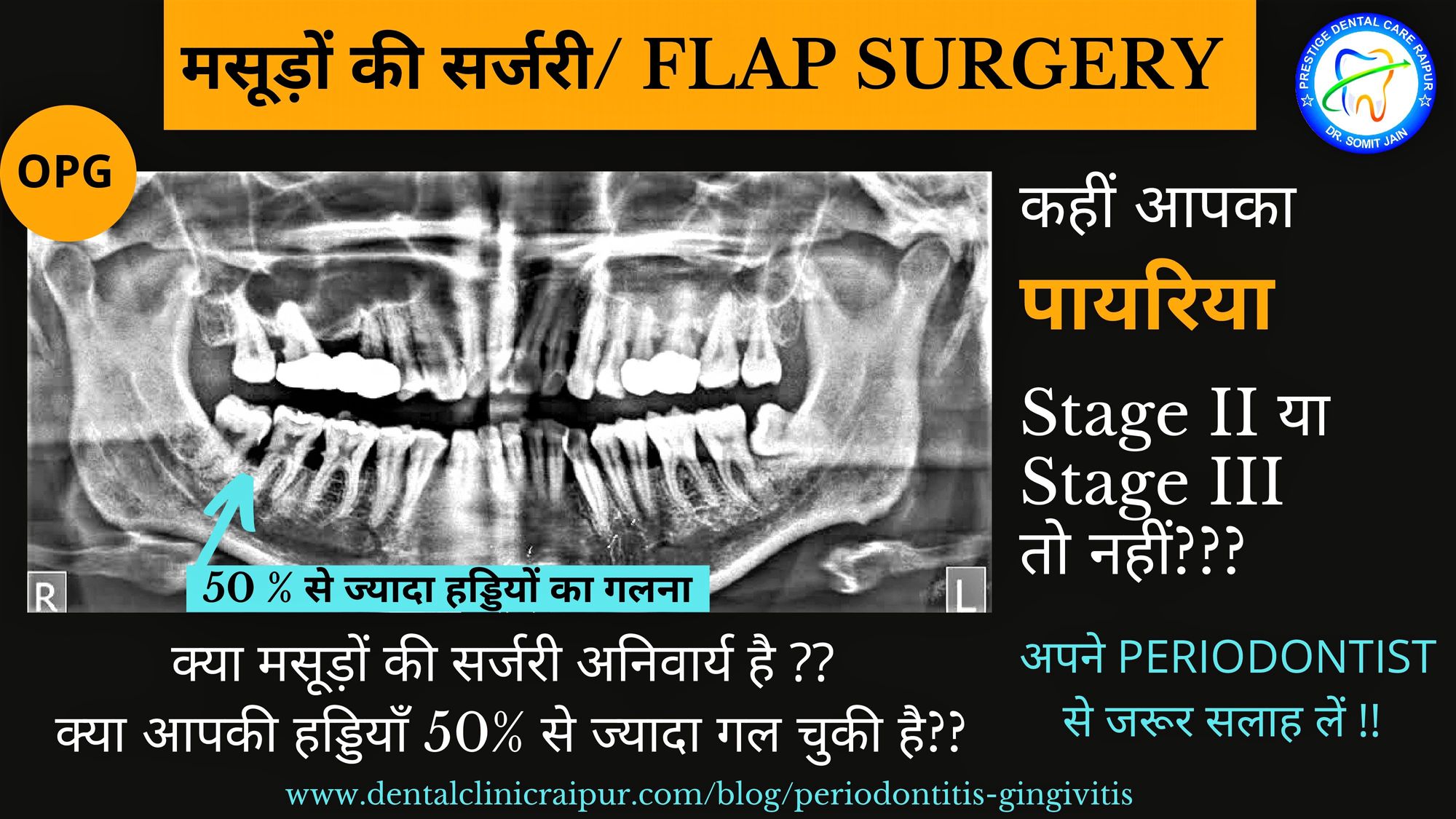
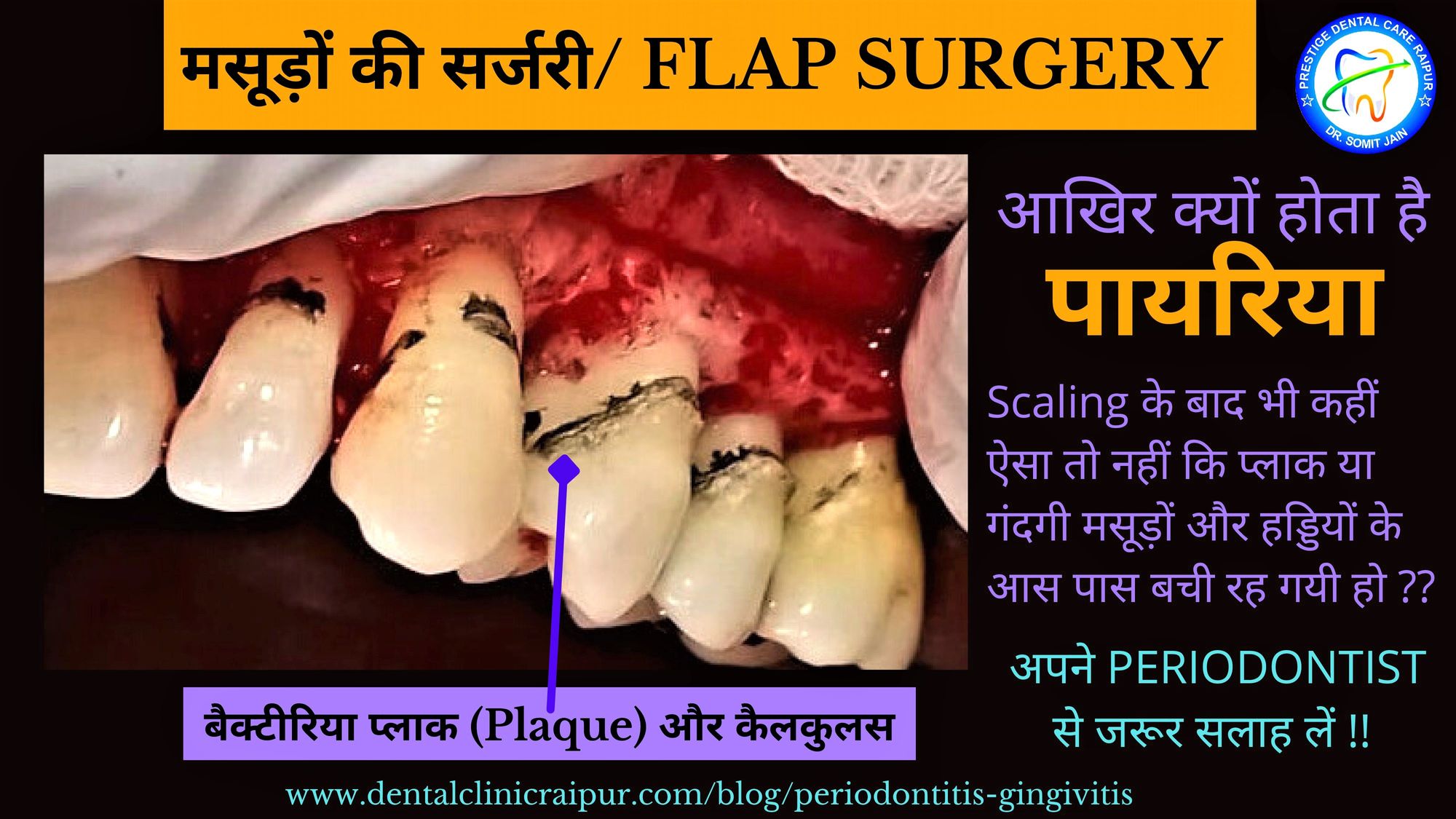
मसूड़ों की सर्जरी / FLAP SURGERY